Abdominal Pain & Bloating: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
- January 10, 2026
- Abrol Hospital
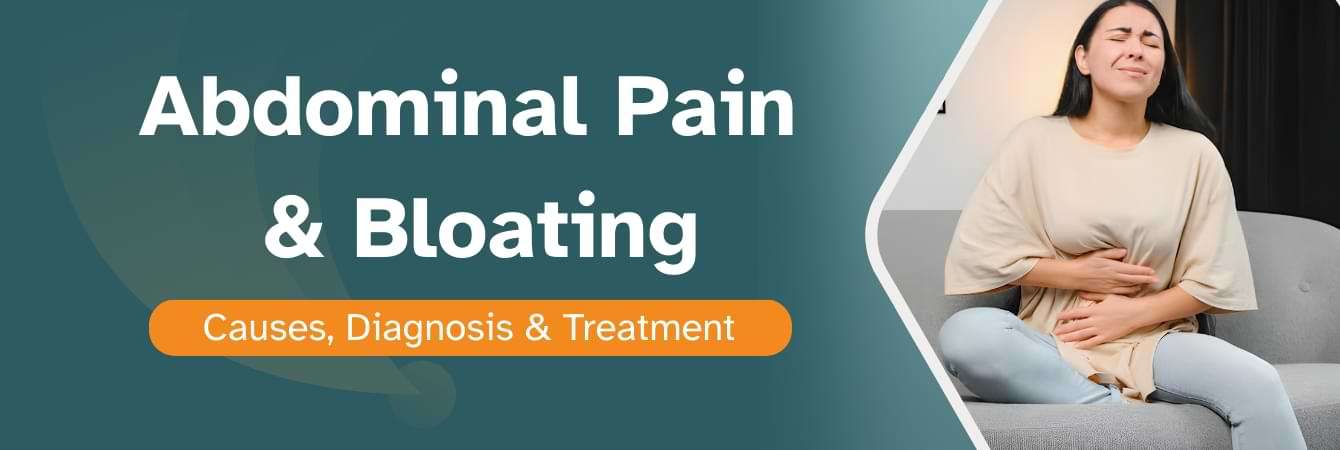
Abdominal pain and bloating are among the most frequent digestive complaints reported worldwide. While occasional stomach pain or belly bloating is usually harmless, persistent or intense abdominal pain may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires professional evaluation.
Understanding Abdominal Pain & Bloating
- Abdominal pain, often described as a stomach ache or abdomen ache, refers to discomfort felt anywhere between the rib cage and the pelvic region. The pain may vary in nature depending on the affected organ, intensity, and duration.
- Bloating refers to the uncomfortable sensation of fullness, tightness, or swelling in the abdomen. Many individuals describe bloating as having a bloated stomach or belly bloating, often accompanied by visible distension and gas.
Types of Abdominal Pain
- Acute abdominal pain develops suddenly and is often severe. It may be associated with conditions such as appendicitis, food poisoning, or gallstones. This type of pain requires urgent medical attention, especially if it worsens rapidly.
- Chronic abdominal pain persists for weeks or months and may come and go. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, or chronic gastritis commonly cause long-term stomach pain and bloating.
- Localized abdominal pain: occurs in one specific area, such as the lower abdomen or upper right side. For example, lower left abdominal pain may be associated with conditions affecting the colon, intestines, or reproductive organs and should be evaluated if persistent.
- Generalized abdominal pain affects a larger area of the abdomen and is often linked to digestive disorders, gas accumulation, or infections.
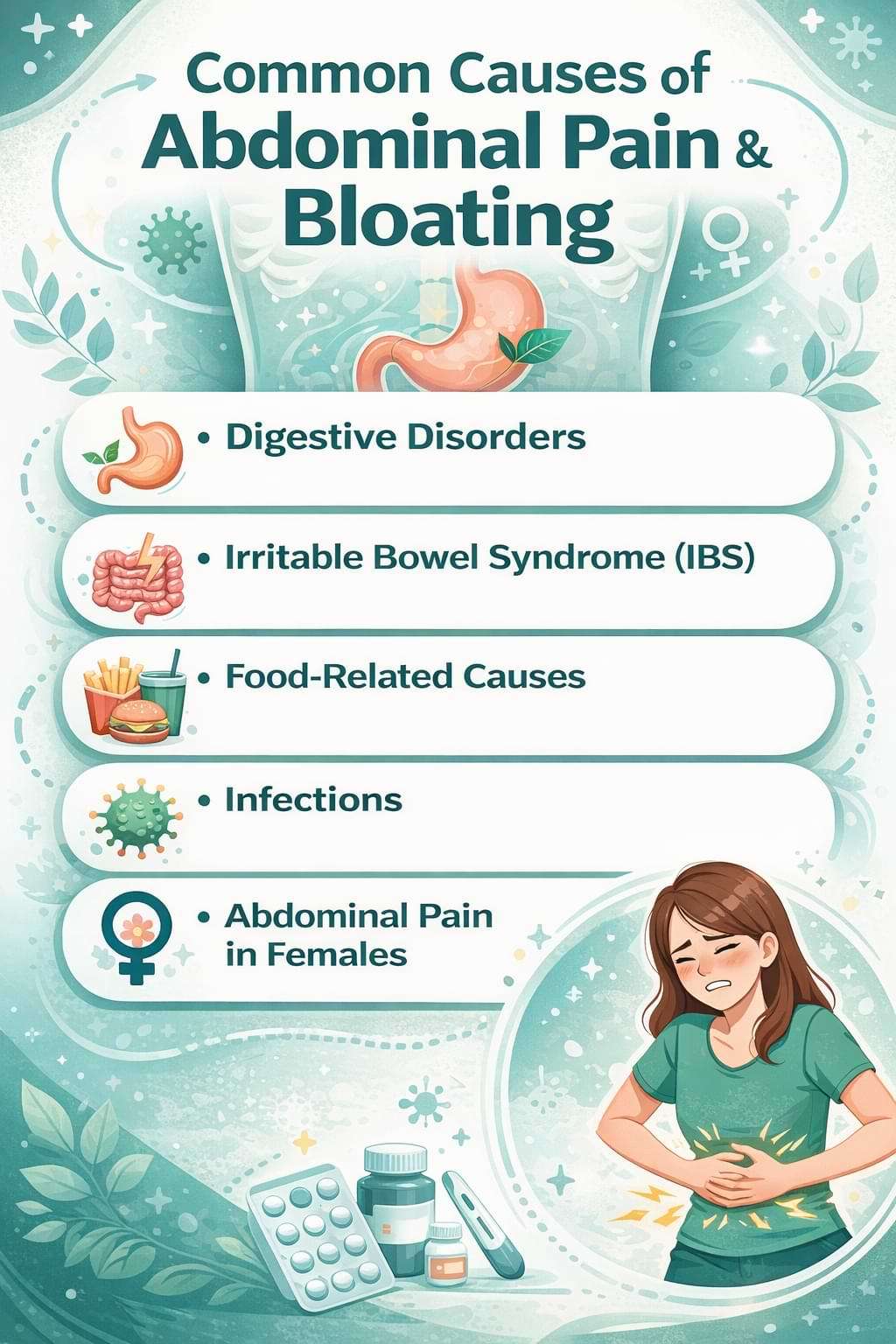
Common Causes of Abdominal Pain and Bloating
- Digestive Disorders:
Digestive conditions are the most common causes of stomach pain and bloating. Indigestion occurs when the stomach struggles to break down food properly, leading to discomfort, fullness, and gas. Gastritis, which is inflammation of the stomach lining, often causes burning pain, nausea, and bloating stomach symptoms.
Read: Best Ways to Improve Digestive System - Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
It is a functional digestive disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. Stress, diet, and gut sensitivity play major roles in IBS-related belly bloating and stomach aches. - Food-Related Causes
Certain foods can trigger abdominal pain and bloating, especially when consumed in excess. Overeating places pressure on the digestive system, causing stomach pain and bloated stomach sensations. Food intolerances such as lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity prevent proper digestion, leading to gas, cramping, and belly bloating. - Infections
Gastrointestinal infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites can result in intense abdominal pain and bloating. Food poisoning often presents with sudden stomach pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal swelling. Parasitic infections may cause chronic gut bloating, weight loss, and persistent discomfort if left untreated. - Abdominal Pain in Females
Abdominal pain in females may be related to reproductive health. Menstrual cramps commonly cause lower abdominal pain and bloating due to hormonal changes. Conditions such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease can lead to recurring abdomen female pain and bloated stomach symptoms.
Treatment Options for Abdominal Pain and Bloating
- Medical Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Acid-reducing medications relieve gastritis and acid reflux. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial infections. Antispasmodic drugs help reduce cramping in IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome), while probiotics improve gut health and reduce gut bloating.
- Dietary Management
Diet plays a crucial role in managing stomach pain and bloating. Eating smaller, frequent meals reduces digestive strain. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods helps prevent recurring belly bloating. Increasing fiber gradually supports bowel health without worsening bloating stomach symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications
Regular physical activity improves digestion and reduces gas buildup. Stress management techniques such as yoga and meditation help alleviate IBS-related abdominal pain. Avoiding smoking, alcohol, and late-night meals also supports digestive health.
Diagnosis of Abdominal Pain and Bloating
Accurate diagnosis begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Doctors assess the location, duration, intensity, and pattern of stomach pain and bloating, along with dietary habits and associated symptoms.
Diagnostic tests such as blood tests help detect infections or inflammation. Imaging studies like abdominal ultrasound or CT scans provide detailed views of abdominal organs. Endoscopy and colonoscopy may be recommended to evaluate the stomach and intestines for ulcers, inflammation, or tumors.
Consult Our Expert Gastroenterologist in Punjab
If you are experiencing persistent abdominal pain, stomach ache, or bloating, do not ignore the symptoms. Early diagnosis can prevent complications and ensure effective treatment.
👉 Consult our experienced Gastroenterologist in Punjab for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment of abdominal pain and bloating. Our specialist uses advanced diagnostic tools and evidence-based treatment approaches to help you achieve long-term digestive health.
📞 Book your consultation today and take the first step toward relief from stomach pain, bloated stomach, and gut bloating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Abdominal Pain & Bloating
The most common causes of abdominal pain and bloating include indigestion, gastritis, acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), food intolerance, infections, and excessive gas formation. In some cases, serious conditions like gallstones or appendicitis may also cause intense abdominal pain and bloated stomach symptoms.
You should consult a gastroenterologist if abdominal pain or bloating lasts more than a few days, becomes severe, or is associated with symptoms like vomiting, blood in stool, fever, or unexplained weight loss. Persistent stomach pain and gut bloating require professional evaluation.
Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as blood tests, ultrasound, CT scan, endoscopy, or colonoscopy. These tests help identify the exact cause of stomach pain and bloating stomach problems.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include medications such as antacids, antibiotics, probiotics, or antispasmodics. Dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and stress management also play a crucial role in relieving belly bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Yes, stress can significantly affect digestion and is a common trigger for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Stress-related digestive issues often cause stomach pain, belly bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
Abdominal pain in females may be linked to menstrual cycles, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or pregnancy, in addition to digestive causes. A gastroenterologist may collaborate with a gynecologist for accurate diagnosis.