Normal Heart Rate: Causes and Risks of Abnormal Heart Rate
- September 2, 2025
- Abrol Hospital
A normal heart rate indicates that your cardiovascular system (heart and the blood vessels) is functioning efficiently, while deviations from the norm can signal underlying medical conditions. Understanding what constitutes a normal pulse rate, the causes of abnormal heartbeats, and the risks associated with conditions like tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, and atrial fibrillation is essential for maintaining heart health and preventing serious complications.
What Is a Normal Heart Rate?
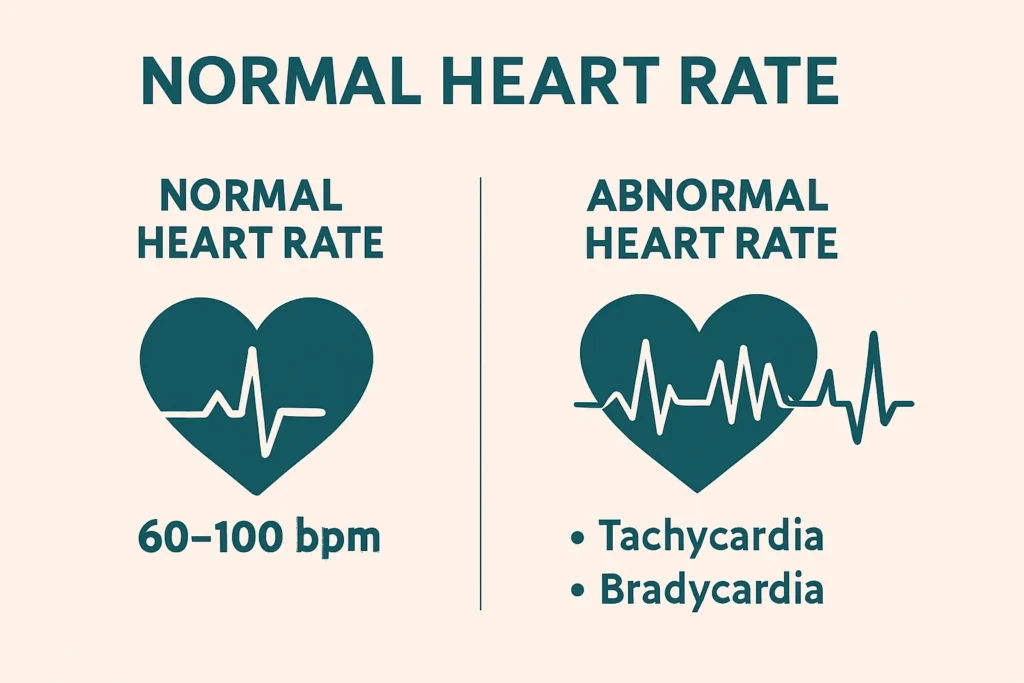
The amount of beats per minute (bpm) that your heart produces when at rest is known as your normal heart rate. This falls between 60 and 100 bpm for the majority of people. However, depending on factors including age, gender, degree of fitness, and general health, this figure may change. For example, because of their increased cardiovascular efficiency, athletes frequently have lower resting heart rates. The normal pulse rate is a vital sign that helps doctors assess the heart’s condition and detect abnormalities early.
Heart rate is influenced by the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary bodily functions. While the parasympathetic branch lowers heart rate at rest, the sympathetic branch raises it during stressful situations or physical exertion. A consistently high or low heart rate outside the pulse rate normal range may warrant medical attention, especially if accompanied by symptoms of Psychosomatic Disorder like dizziness, fatigue, or chest pain.
Normal Heart Rate for Women by Age
Women typically have slightly higher resting heart rates than men due to hormonal differences and smaller heart size. As women age, their normal heart rate tends to decrease gradually. For example, a woman in her 20s may have a resting heart rate of 70–90 bpm, while a woman in her 60s may average around 60–70 bpm. These variations are considered normal unless accompanied by symptoms of arrhythmia or cardiovascular distress.
Factors such as pregnancy, menopause, and hormonal fluctuations can also affect a woman’s heart rate. During pregnancy, for instance, the heart works harder to supply blood to the growing fetus, often resulting in a temporary increase in pulse rate. Postmenopausal women may experience changes in heart rhythm due to declining estrogen levels, which can impact vascular health and heart function.
Normal Heart Rate for Men
Men generally have a lower resting heart rate compared to women, often ranging from 60 to 80 bpm. This is partly due to larger heart size and higher levels of hemoglobin, which allow for more efficient oxygen transport. Age and level of fitness can also affect a man’s normal heart rate. Younger men and athletes may have resting heart rates as low as 40–60 bpm, which is considered healthy if not accompanied by symptoms.
As men age, their heart rate may increase slightly due to reduced cardiovascular efficiency. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and lack of exercise can further influence heart rate. Monitoring changes in pulse over time can help detect early signs of heart disease, especially in men over 50 who are at higher risk for conditions like hypertension and coronary artery disease.
What Is an Abnormal Heartbeat?
An abnormal heartbeat, also known as an arrhythmia, occurs when the heart beats too fast, too slow, or irregularly. These deviations from the normal heart beat can be harmless or indicative of serious health conditions. Arrhythmias are classified based on their origin and pattern. Common types include tachycardia (fast heartbeat), bradycardia (slow heartbeat), and irregular rhythms such as atrial fibrillation.
Symptoms of abnormal heartbeats vary widely. Some people may feel palpitations, fluttering in the chest, or skipped beats, while others may experience fatigue, dizziness, or fainting. Arrhythmias can cause unexpected cardiac arrest, heart failure, or stroke in extreme situations. In order to manage these illnesses and avoid consequences, early detection and treatment are essential.
Causes of Abnormal Heartbeats
Abnormal heartbeats can result from a wide range of factors, including medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these causes is key to prevention and effective treatment.
🩺 Medical Conditions: Heart disease, high blood pressure, thyroid disorders, and diabetes are common culprits of arrhythmias. Structural abnormalities in the heart, such as valve defects or scarring from previous heart attacks, can disrupt electrical signals and lead to irregular rhythms. Infections like myocarditis or pericarditis may also affect heart function. Identifying and managing these conditions through regular check-ups and appropriate treatment can reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
💊 Medications and Substances: Certain medications, including decongestants, asthma inhalers, and antidepressants, can trigger abnormal heartbeats. Stimulants like caffeine and recreational drugs such as cocaine or amphetamines are known to increase heart rate and cause arrhythmias. Alcohol abuse can lead to a condition known as “holiday heart syndrome,” where binge drinking causes AFib. It’s important to review medications with a healthcare provider and avoid substances that may affect heart rhythm.
🧠 Lifestyle Factors: Stress, poor sleep, and sedentary habits contribute significantly to heart rhythm disturbances. Chronic stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, increasing heart rate and blood pressure. Smoking damages blood vessels and affects oxygen delivery, while lack of exercise weakens the heart muscle. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle—including regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and stress management—can help maintain a normal heart rate and prevent arrhythmias.
Understanding the root causes helps in prevention and treatment.
Strong Heart, Safe Future—Consult our Cardiologist Today
If you’re experiencing irregular heartbeats, chest discomfort, or just want to understand your heart health better, don’t wait. Consult our expert cardiologist, for personalized care and early diagnosis. Call or visit Abrol Hospital, Gurdaspur to book your appointment today—your heart deserves the best.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Yes, 80–90 bpm falls within the normal range, though it's on the higher side of resting heart rate.
elow 50 bpm (bradycardia) or above 100 bpm (tachycardia) at rest may be concerning.
Above 120 bpm at rest could signal arrhythmia or other cardiac issues.
Seek medical attention if accompanied by dizziness, chest pain, or shortness of breath.
Yes, anxiety activates the sympathetic nervous system (fight-or-flight response), which can raise your heart rate temporarily—even at rest.
Common triggers include:
Stress or panic attacks
Fever or dehydration
Caffeine or stimulant medications
Arrhythmias or thyroid issues
Yes, during exercise, stress, or illness, both can increase. However, they are regulated independently and don’t always rise or fall together



